Rigid Flex Rigid PCBs for Specialty Industries
Rigid Flex Rigid PCBs for Specialty
Rigid flex rigid pcbs are popular among manufacturers who need circuit boards with high reliability, compact size, and unique shape. These PCBs can also be used for specialized applications such as military devices, medical products, aerospace equipment, and more. Rigid flex PCBs offer several advantages over traditional PCBs, including improved heat dissipation and reduced electromagnetic interference (EMI). These are important factors for critical industries like the military and medical, where safety and durability are key.
Rigid-flex PCBs are typically thin and light, enabling them to fit inside even the most constrained spaces. These circuits are often designed in 3D, allowing them to bend or twist into different shapes. In addition, rigid-flex circuits have a lower total volume than rigid PCBs and are less expensive to produce.
In general, rigid-flex PCBs can benefit nearly all electronics industries, but some common applications include medical devices, aerospace equipment, and automotive electronics. In the medical industry, for example, rigid-flex PCBs are commonly used in devices such as pacemakers, cochlear implants, and handheld monitors. In the aerospace industry, rigid-flex circuits are often used for flight control systems, radar equipment, and communication equipment.
These circuit boards can be made from a wide variety of materials, and they may have either single- or double-sided circuit patterns. They can be etched using various methods, such as dipping in an etch bath or spraying the surface with an etchant solution. Then, they’re drilled using mechanical means, such as laser drilling, and copper is deposited to establish electrical connections. Finally, a layer of cover lay and adhesives are applied to the top.
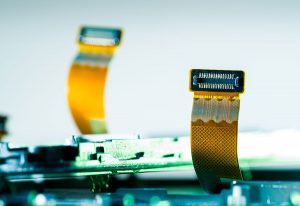
Rigid Flex Rigid PCBs for Specialty Industries
The most common construction for a rigid flex rigid pcb is a stackup of four rigid layers and two flexible sections. The rigid sections are usually built from FR-4 fiberglass and have polyimide film for insulation. The flex section includes two layers of prepreg and coverlay to connect to the rigid sections. Manufacturers then apply a solder mask to the boards to protect them from contaminants and reduce corrosion.
Compared to standard rigid PCBs, rigid-flex circuits can provide better current carrying capacity. This makes them suitable for high-speed data communication and industrial equipment. Additionally, they can reduce the number of interconnections, which reduces noise and electromagnetic interference.
Rigid-flex circuits are a good choice for any application that requires a combination of flexibility and space efficiency. They’re particularly well suited for small electronic devices and consumer products. These circuits can minimize space and weight while providing improved reliability, reducing the need for solder joints and jumper wires. Additionally, they can withstand vibration and shock, making them ideal for use in mobile phones and digital cameras. However, it’s worth noting that rigid-flex circuits are more expensive than traditional PCBs and fully flexible circuits. For this reason, they’re best suited for critical applications where safety and reliability are paramount.